Summary Week 8
1. Routh-Hurwitz Method
-
method for determining the number of roots of a given polynomial that have
positive real parts.
-
Procedure: build the Routh-Hurwitz array, and then count the number of
sign changes that occur in reading the first column from top to bottom.
-
Applications:
-
Used for establishing the stability of a transfer function, if the polynomial
being considered is the characteristic polynomial (i.e. denominator polynomial).
Specifically, in cases where a design or control tuning parameter appear
in the coefficients of the polynomial, the Routh Hurwitz can detect the
acceptable ranges of these parameters (or even nonexistence of values)
for which the system is stable.
-
Could also be used to detect the critical values of the parameters which
could yield pure imaginary roots, as may be needed in a Ziegler-Nichols
tuning approach.
2. Final Value Theorem.
Given L[x] = f(s), the value of
x at t=¥ can be found without
having to invert f(s) first, via the following fact :
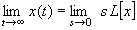
provided all the characteristic roots (i.e. roots of the denominator
of
L[x]) have negative real parts.
3. Review for Exam 2